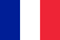
Cervical osteochondrosis is a common degenerative-dystrophic disease that develops in the cervical spine. In women, a weak muscular corset, as well as thin bone tissue, lead to faster development of pathology. The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women are pronounced. When they occur, treatment should be started immediately.
Causes of cervical osteochondrosis in women
Cervical osteochondrosis in women can develop in the presence of various provoking factors. The development of pathology is diagnosed regardless of the age of the patient. The causes of osteochondrosis in women are:
- Insufficient physical activity;
- sedentary work;
- Sedentary lifestyle.
The occurrence of pathology of the cervicothoracic region is diagnosed by frequent hormonal failures. If the load on the spine increases during the birth of a child, then this leads to the appearance of this disease. Improper nutrition throughout life becomes a cause of metabolic disorders. All this leads to the development of diseases.
Older women are at risk of developing the disease. A fairly common cause of osteochondrosis is hypothermia. The disease can develop with injury. Injuries are diagnosed with the occurrence of disc disease in women. Pathology often develops against the background of infectious processes.
Osteochondrosis in the fairer sex develops under the influence of various factors. So you have to take responsibility for your health.
Signs of osteochondrosis in women
Signs of osteochondrosis in women appear after a certain time after the beginning of the degenerative process. It is not uncommon for vertebrae to protrude from their boundaries, leading to a worsening of the situation as they become thinner in parallel. Against the background of inflammatory processes in the intervertebral discs, pain is diagnosed, which can be permanent or temporary.
During the disease, brain tissue is damaged, which causes headaches. Dizziness may be diagnosed when squeezing the vertebral artery with cervical osteochondrosis. Changes in blood pressure are not uncommon in women of the weaker sex. During the development of cervical osteochondrosis, women may experience fainting.
In some cases, with pathology, patients have hearing loss. During osteochondrosis in women, the symptoms are manifested in the form of a change in gait. The pathological process leads to frequent mood swings. Most patients are diagnosed with severe fatigue even when performing daily tasks. Symptoms may manifest as decreased vision. When the disease significantly worsens the condition of the teeth, which leads to the development of various dental diseases. Some people are diagnosed with back and neck muscle cramps. With this pathology, the intensity of the voice may decrease.
The disease negatively affects the state of the brain, leading to deterioration of memory and thought processes. Some patients experience snoring during sleep. This is due to the fact that during sleep, there is tension in the neck muscles. The most common of the symptoms is radicular syndrome. Its appearance is diagnosed when the nerves in the cervical vertebrae are compressed.
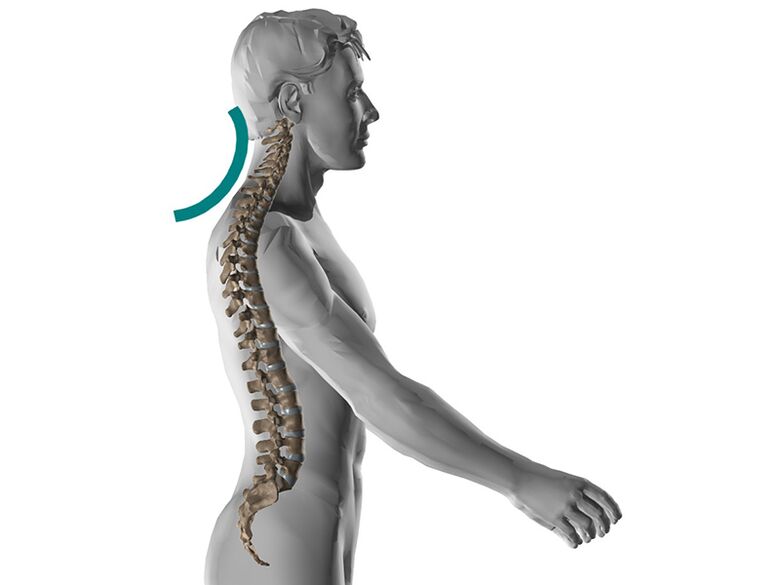
Since the disease affects the nervous system, it leads to numbness of the fingers, which makes it impossible to perform the most important tasks related to fine motor skills. Symptoms manifest as weakness in the hands. If osteochondrosis of the thoracic or lumbar region is diagnosed, then it leads to back pain. If the cervical region is affected, the head or neck suffers. The pain can spread to the back as well as the limbs. Sleep disorders are often diagnosed.
After the age of 50, the signs of osteochondrosis in women are more pronounced.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in women
When symptoms appear, cervical osteochondrosis in women should be treated immediately. First of all, it eliminates joint pain. Appropriate examinations should be performed before treating osteochondrosis in women. This will make it possible to determine a rational treatment.
The main treatment begins only after the patient undergoes a complete examination. The most common methods of treating joints include drug therapy. In that case, the use of local preparations is recommended.
When the disease occurs, the main treatment begins only after consulting a doctor. If topical preparations are not effective enough, then the use of tablet forms of drugs is recommended. In most cases, after such treatment, the pain completely disappears. If severe muscle pain is observed, anesthetic injections are recommended.
In addition to relieving pain, the main treatment helps in most cases. But to improve its effectiveness, you can use folk methods. The use of painkillers in the shoulder joint and neck is recommended. Features of the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis require the use of massage, drug treatment, folk methods. Physical therapy is also effective. In addition to the ineffectiveness of gymnastics, yoga and other therapeutic methods are prescribed. It is also recommended to treat the disease with a method such as water aerobics.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid the development of pathology, it is recommended to carry out its prevention in a timely manner. It consists of following a series of simple rules. Regular exercise is recommended to help develop the upper shoulder girdle, as well as strengthen the back. Sufficient physical activity will enable a woman to avoid the disease. Regular outdoor walks are recommended.
Swimming is an effective preventive method. If a woman has a sedentary job, then she is recommended to get up regularly and do exercises. Every woman should have a rational and proper diet. It is recommended to eat foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals. When the first signs of a pathological process appear, it is necessary to seek the help of a doctor. Timely identification of the pathological process is the key to successful treatment of the pathology.
Osteochondrosis is characterized by severe degenerative changes in cartilage and joints. In women, the pathology is accompanied by pronounced signs. When the first signs appear, the patient should consult a doctor who will prescribe rational treatment after the appropriate diagnosis.